Example Test "Ice Cream Sale" - Considering Follow-up Mistakes
Example test ice cream sale
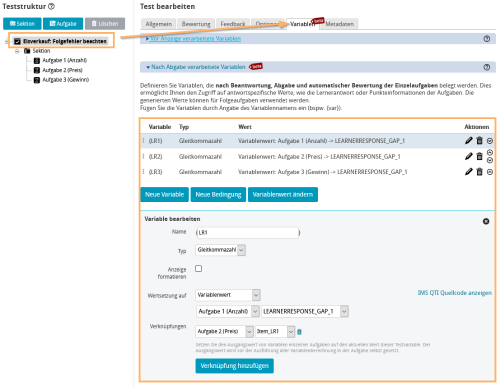
| Test variables: In the example, “post-processed” (post) variables will be created at test level and set to the value of the learner response for each question. For example, the test variable {LR1} will be set to the value of the learner response, i. e. the entry of the participant, for the first question. By assigning learner responses to variables of subsequent questions, you can use these learner responses continuously over multiple questions. More specifically, the value of the test variable {LR1}, i. e. the learner response to the first question, will be passed to the variable Item_LR2 of the second question. |
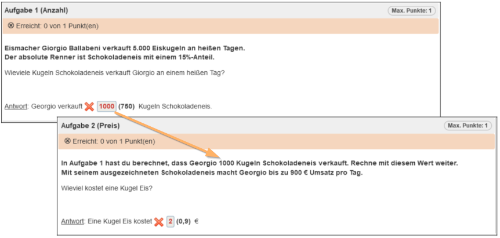
Display of the individual hint during the test:
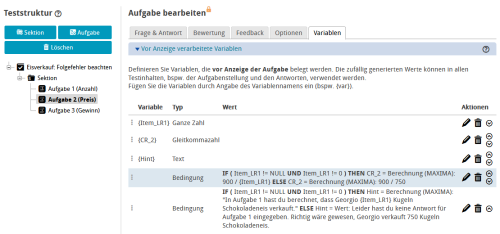
| Question variables and calculation of follow-up mistakes: The value of the question variable Item_LR1 will be initialised by the test system. Upon the submission of the first test question, the learner response will be stored in the post-test variable LR_1. When the second question opens, this value will be passed on to question 2 due to the assignment to the question variable Item_LR1. Whether or not a learner response has been entered for question 1 will be checked using a condition:
Creation of an individual hint: The auxiliary variable “Hint” allows you to generate an individual hint for the participant. It will again be checked with a condition whether or not the participant has entered a response for question 1.
|
Creating a simple example step by step
Follow these steps to create a simple example for displaying the learner response in the subsequent question:
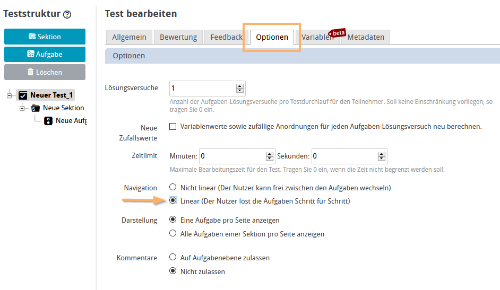
1 | Create a test. In the options tab, enable linear processing for the test. Linear processing ensures that participants process the questions one after the other. Only if this setting has been configured, it will be possible to pass on values from one question to the next. |
|
2 | Create two text entry interactions titled A1 and A2. |
|
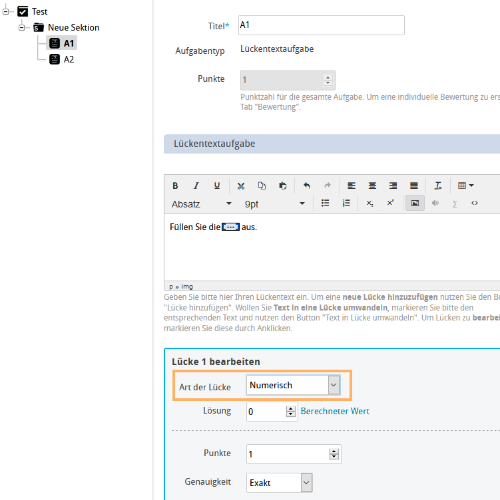
3 | Specify the gap type for the first question, for example "Numeric (floating point)". |
|
4 | Then create a pre-question variable (Item_LR1) with an empty value for the second question. This question variable will be necessary to record the learner response from A1. The assignment will be done in step 6. The variable type must match the selected gap type for question A1:
|
|
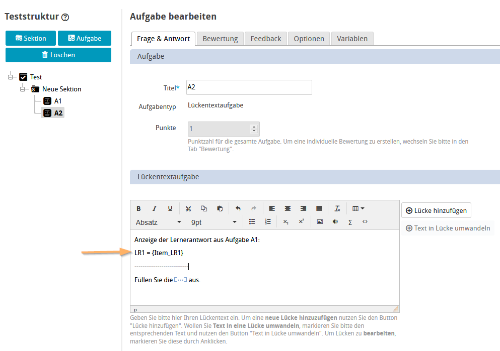
5 | To display the pre-question variable (Item_LR1) and thus the participant response from the first question (A1) later in the question text of question A2, you need to insert it in the question text. |
|
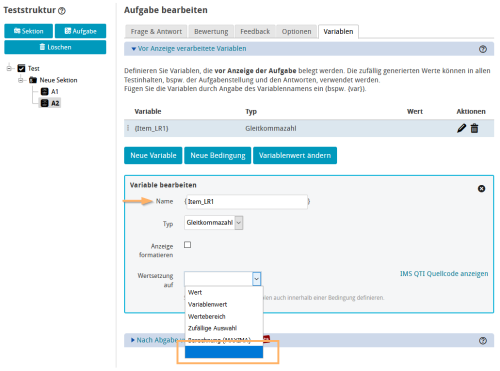
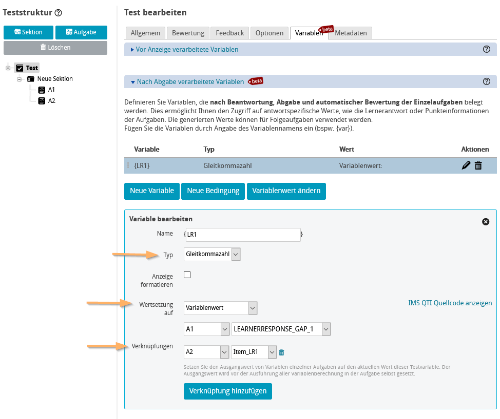
6 | Now create the post-test variable (LR1). Do not forget to pay attention to choosing the correct variable type here as well. In the example, the type "Floating point" is used. Set the value of the variable to the variable value of the learner solution (LEARNERRESPONSE_GAP_1) for question A1. Assign this post-test variable to the question variable (Item_LR1). |
|
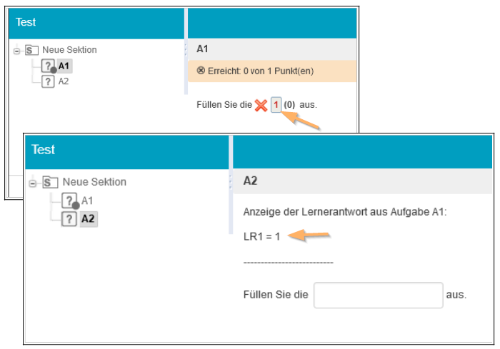
7 | Save the test and start the preview. Fill in the blank of the first question. Then switch to the second question. The value entered in the first question will be displayed in the question text. |
|