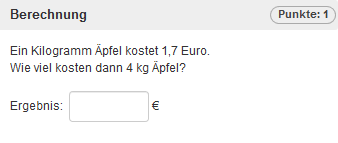
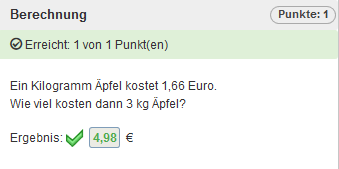
Berechnungsaufgabe (Lückentext)
Schritt für Schritt
Im Folgenden wird die Erstellung einer Berechnungsaufgabe, anhand der abgebildeten Beispielaufgabe erklärt.
Schritt 1: Konzeption der Aufgabe
Als Beispiel soll eine Berechnungsaufgabe mit einer gegebenen Funktion erstellt werden. Der Lernende soll die Fläche unter dieser Funktion in einem gegebenen Intervall berechnen. Als Parameter dienen die Faktoren der Funktionsgleichung und die Intervallgrenzen. Alle Parameter sollen als zufällige, ganzzahlige Werte in einem gegebenen Intervall ermittelt werden.

Schritt 2: Definition der Parameter
Wechseln Sie in das Tab „Variablen“ und erstellen Sie vier neue Variablen. Vergeben Sie als Variablen-Name entsprechend dem Konzept die Identifier „a“, „b“, „c“ und „d“. Alle Variablen sind vom Typ „Ganze Zahl“. Zur Wertermittlung nutzen wir die Funktion „Zufällige Auswahl“ und definieren einen Wertebereich.
Für den Einsatz von Konstanten verwenden Sie auch "Zufällige Auswahl" und geben anschließend nur den einzelnen Wert für die zu verwendende Konstante vor.
Eine detaillierte Beschreibung zum Anlegen und Einfügen von Variablen erhalten Sie in der Hilfe-Beschreibung zur Verwendung von Variablen.

Abb: Variable definieren
Schritt 3: Erstellung der Aufgabenstellung
Wechseln Sie in das Tab „Frage & Antwort“ und geben Sie die Fragestellung in das Textfeld ein. Formeln können Sie mit LaTeX direkt in den Aufgabentext integrieren (Hilfe zur Formeleingabe). Um die definierten Variablen als Parameter in der Funktion zu nutzen, geben Sie einfach an die entsprechende Stelle den Variablennamen in geschweiften Klammern ein (bspw. {a}). ONYX erkennt automatisch, dass es sich um eine definierte Variable handelt und ersetzt diese entsprechend bei der Testdurchführung. Die Angabe von Variablennamen ist innerhalb von LaTeX, als auch im normalen Text möglich.

Abb: Erstellung Aufgabenstellung
Schritt 4: Erstellung der Berechnungsvorschrift
Klicken Sie mit der Maus auf das Lückensymbol ![]() oder erstellen Sie eine neue Lücke mit Hilfe des Buttons „Lücke hinzufügen“. Es öffnet sich das Bearbeiten-Fenster für die gewählte Lücke. Wählen Sie nun die Option „Neue Variable definieren“. Sie gelangen automatisch zum Tab Variablen und es wurde eine neue Variable mit dem Identifier „solution“, vom Typ „Ganze Zahl“ (oder „Gleitkommazahl“) erstellt. Zur Wert-Ermittlung ist bereits die Option „Berechnung“ ausgewählt. Da wir als Lösung eine „Gleitkommazahl“ erwarten, wechseln wir den Typ nach „Gleitkommazahl“. Geben Sie nun die Berechnungsvorschrift in das vorgesehene Eingabefeld ein. Verwenden Sie auch hier die Parameter durch Angabe des Variablennamens in geschweiften Klammern (bspw. {a}). Die Berechnungsvorschrift wird in MAXIMA-Schreibweise angegeben.
oder erstellen Sie eine neue Lücke mit Hilfe des Buttons „Lücke hinzufügen“. Es öffnet sich das Bearbeiten-Fenster für die gewählte Lücke. Wählen Sie nun die Option „Neue Variable definieren“. Sie gelangen automatisch zum Tab Variablen und es wurde eine neue Variable mit dem Identifier „solution“, vom Typ „Ganze Zahl“ (oder „Gleitkommazahl“) erstellt. Zur Wert-Ermittlung ist bereits die Option „Berechnung“ ausgewählt. Da wir als Lösung eine „Gleitkommazahl“ erwarten, wechseln wir den Typ nach „Gleitkommazahl“. Geben Sie nun die Berechnungsvorschrift in das vorgesehene Eingabefeld ein. Verwenden Sie auch hier die Parameter durch Angabe des Variablennamens in geschweiften Klammern (bspw. {a}). Die Berechnungsvorschrift wird in MAXIMA-Schreibweise angegeben.
Im Tab „Frage und Antwort“ wurde als Lösung automatisch die neue Variable „solution“ ausgewählt.

Abb: Berechnungsvorschrift
Schritt 5 (optional): Definition eines Toleranzbereiches
Um bei „Gleitkommazahlen“ unabhängig von der Genauigkeit des Ergebniswertes, eine beispielsweise auf zwei Dezimalstellen genau Lösung abzufragen, definieren wir eine absolute Abweichung von „0,01“, ohne Einbeziehung der Toleranzgrenzen.
Eine detaillierte Beschreibung zur Option „Genauigkeit“ erhalten Sie in der Hilfe-Beschreibung zur Numerischen Eingabe.

Abb: Toleranzbereichen festlegen
Schritt 6: Überprüfung der Aufgabe
Wählen Sie nun die Option „Vorschau“, um eine zufällig generierte Beispielaufgabe Ihrer Berechnungsvorschrift anzuzeigen. Bei jedem Aufruf der Vorschau wird die Aufgabe neu generiert. Die Vorschau bietet Ihnen auch die Möglichkeit zur Überprüfung der Lösungseingabe.

Abb: Überprüfung der Aufgabe
Beispiel Gleitkommazahlen
Ziel: In einer Aufgabe soll eine ganze Zahl mit einer Gleitkommazahl multipliziert werden.
Anlegen eine Berechnungsaufgabe und Definition von Variablen:

Formulierung der Fragestellung zur Multiplikation der angezeigten Werte:

Die Auswertung der Nutzereingabe erfolgt in der Standarteinstellung mit "exakter" Genauigkeit:

Der Nutzer kann keine richtige Lösung eingeben. Die Variable mit der Gleitkommazahl wird in diesem Fall mit 4 Nachkommastellen angezeigt. Die exakte Berechnung erfolgt jedoch mit dem exakten Zufallswert der Variable.

Lösung: Mit der Einstellung "Genauigkeit: Absolut" wird ein Toleranzbereich für die Berechnung der Lücke definiert.

Mit der Wahl eines geeigneten Intervalls wird das Ergebnis richtig bewertet.